Page 93 - MA - May 2017
P. 93
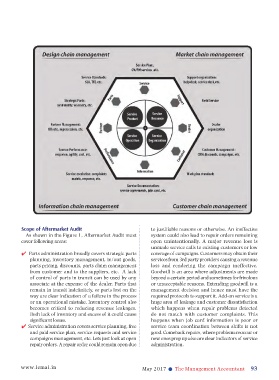
For a comprehensive aftermarket audit, we propose
auditing of four arrays of service: service product,
service resources, service organization, and service
operations (Armistead & Clark 1991, Cohen et al.,
2006). This framework is based on Institute of Cost
and Works Accountants of India (ICWAI) 2009
guidelines for an internal audit. An aftermarket audit
is an appraisal of company’s aftermarket operations,
evaluation and monitoring of risk management,
reporting and control practices. As an internal
audit, aftermarket audit provides inputs on: control
environment, risk assessment, control actions,
information and communication and monitoring of
complete gamut of aftermarket activities. We therefore
recommend an aftermarket audit to capture:
Service product encompasses identification of
what strategic parts does the organization want to
support, what are the service policies, aftermarket
parts sales, committed free offerings, warranty
cover, and the complete service plan.
Service resources would entail the of field and off-
field service resources, technicians, mobile service
vans, mobile tools and fixtures, and their work
plans. Work plan administration also includes
workshop service, planned services, service
training and certification, Bay management, etc.
Service organization refers to the dealer and OEM
support network including help desk, service desk, Scope of Aftermarket Audit to justifiable reasons or otherwise. An ineffective
parts desk, etc. Service organization would also As shown in the Figure 1, Aftermarket Audit must system could also lead to repair orders remaining
define the service standards, customer complaint cover following areas: open unintentionally. A major revenue loss is
management, campaign management, and CRM. unmade service calls to existing customers or low
Parts administration broadly covers strategic parts coverage of campaigns. Customers may obtain their
Service operations include the service planning, inventory management, in/out goods, services from 3rd party providers causing a revenue
documentation, partner management for fill parts pricing, discounts, parts claim management loss and rendering the campaign ineffective.
rate, and availability, service protocols and service from customer and to the suppliers, etc. A lack Goodwill is an area where adjustments are made
performance. of control of parts in transit can be used by any beyond a certain period and sometimes for frivolous
Figure 1 presents the scope and details of an associate at the expense of the dealer. Parts that or unacceptable reasons. Extending goodwill is a
aftermarket audit. This can be used at either an OEM remain in transit indefinitely, or parts lost on the management decision and hence must have the
level or OEM and its constituents (Dealers, partners). way are clear indication of a failure in the process required protocols to support it. Add-on service is a
or an operational mistake. Inventory control also huge area of leakage and customer dissatisfaction
Aftermarket audit must capture becomes critical to reducing revenue leakages. which happens when repair problems detected
Both lack of inventory and excess of it could cause do not match with customer complaints. This
Lack of SOP adherence significant losses. happens when job card information is poor or
Operational problems Service administration covers service planning, free service team coordination between shifts is not
Mismanagement and paid service plan, service requests and service good. Comeback repairs, where problems reoccur or
Irregularities campaigns management, etc. Lets just look at open new ones prop up also are clear indicators of service
Lack of controls repair orders. A repair order could remain open due administration.
www.icmai.in May 2017 l The Management Accountant 93